The lab’s latest publication focuses on Hoplobatrachus chinensis, a frog species that lives mainly in plains and hilly landscapes at altitudes between 20 and 1120 m. It is commonly found in moist habitats such as agricultural wetlands, ditches, and ponds in East and Southeast Asia. The species is generally present in rice paddies and their surrounding areas, as rice paddies provide the necessary conditions for development, growth, and breeding, such as shallow, slow-moving water bodies, surrounded by moist surface soils, abundant food sources, and adequate sheltering micro-habitat. In recent decades, due to human disturbance, over-harvesting, and ecological degradation, H. chinensis has declined sharply in population density and distribution area.

Therefore, in order to explore the effects of climate change and dispersal ability on the range of H. chinensis and its occupation of agricultural wetlands, we use survey records and secondary sources (Global Biodiversity Information Facility database), together with climate, geography and vegetation data, to build environmental niche models in MaxEnt and dispersal models in MigClim to assess the impacts of climate change and dispersal ability on the range of H. chinensis. Based on the model results, we calculated the overlap between suitable habitats and agricultural wetlands.
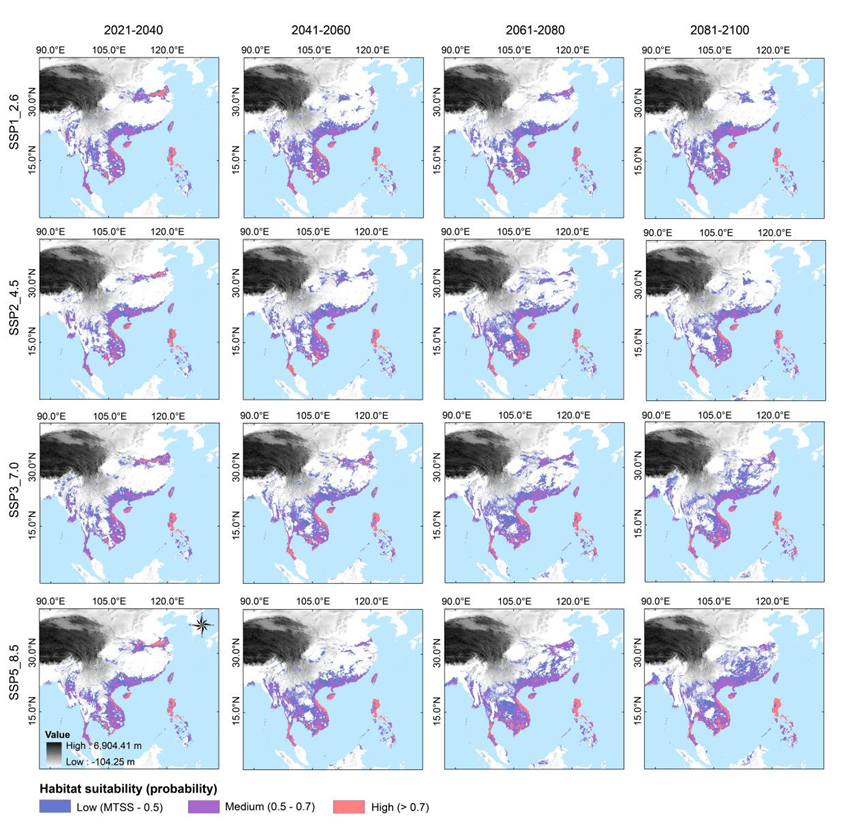
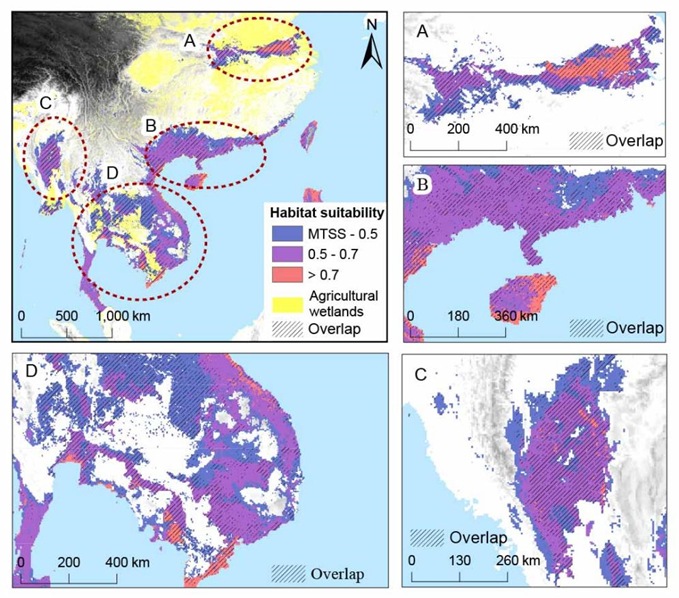
The models indicated that temperature was a key factor affecting H. chinensis distribution. Increasing temperatures positively correlated with habitat suitability, with suitable habitat expanding northward by 2060 while maintaining suitability in the southern parts of the range. We found a 25.18% overlap between the current potential suitable habitat of H. chinensis and agricultural wetlands. MigClim model indicated that H. chinensis might be able to track shifts in suitable habitats under climate change given a 15 km dispersal ability per generation. Climate change will likely expand suitable habitat for H. chinensis. Our predictions offer important guidance for the conservation of the species, especially for the integrated role of natural and agricultural wetlands such as rice paddies.
To read more, the paper is free to read at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.110732.
Highlights
Temperature is a key factor affecting the distribution of Hoplobatrachus chinensis
Climate change will expand the suitable habitat of Hoplobatrachus chinensis
The species has a 25% overlap between suitable habitats and agricultural wetlands
H. chinensis might be able to track shifts in suitable habitats under climate change

